chlamydia in cats vaccine
Chlamydophila felis is a type of bacteria that mainly causes conjunctivitis in cats. However infection is common see above and it can cause significant distress to affected cats which justifies consideration of inclusion of Chlamydophila in routine vaccination protocols.
Nobivac Feline 1 Hcpch Eclipse 4 Revival Animal Health
Feline chlamydial conjunctivitis is an infection caused by a bacterial organism called Chlamydophila felis.
/adult-cat-vaccination-schedule-4846632_V4-ff36ccb34d74410d9652b4307a26e8b3.png)
. In rare cases a much more virulent strain of this virus can cause inflammation of the liver intestines pancreas. Vaccines are available for chlamydiosis in cats. This vaccination combination is commonly.
The noncore vaccines include. A commercially available modified live chlamydial vaccine against feline pneumonitis was tested in 26 cats for its ability to protect against aerosol challenge exposure to the feline pneumonitis strain of Chlamydia psittaci. A vaccine is available in many countries to protect cats against chlamydophila conjunctivitis.
Although not generally suitable for the majority of pet cats it can be useful in high risk situations such as catteries with persistent problems with the organism. This does not always prevent infection but is helpful in preventing severe clinical disease. Depending on the disease the vaccine will.
Vaccines that may be considered as noncore include those against bacterial diseases caused by Chlamydia felis and Bordetella bronchiseptica in addition to the infections caused by feline leukemia virus FeLV feline immunodeficiency virus and feline coronavirus. Affected cats may experience sneezing eye and nasal discharge conjunctivitis lethargy loss of appetite sores on the gums and soft tissues of the oral cavity and lameness. Veterinarians routinely recommend certain vaccines for all cats called core vaccines whereas others are used more selectively according to the cats environment and lifestyle.
Diagnosis can be confirmed by demonstration of intracytoplasmic inclusions in exfoliative cytologic preparations by isolation of the Chlamydophila organism in cell culture or by PCR for DNA on conjunctival swabs. Cats that have developed this infection will often exhibit traditional signs of an upper respiratory infection such as watery eyes runny nose and sneezing. Non-core vaccines Feline leukaemia virus FeLV.
Transmission of avian C psittaci strains to people may result in atypical pneumonia or even life-threatening acute illness ie psittacosis in people. Vaccines work by stimulating the bodys immune system to recognize and fight a particular microorganism such as a virus bacteria or other infectious organism. First of all a vaccine against it does exist and since this is a bacterial condition it is quite effective.
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Vaccine The FIV vaccine was an inactivated adjuvented dual subtype vaccine that was released in July 2002. After cats were challenge exposed 30 days after vaccination pyrexia of greater than 400 C occurred in 81 of nonvaccinated control cats and in 13 of. C pecorum is a ubiquitous cause of ocular infections in livestock although the overall contribution to infectious conjunctivitis is unclear.
Routine vaccination of pet cats is sometimes questioned usually on the basis that the disease caused by Chlamydophila felis is treatable and not life threatening. Transmission between companion parrots and dogs or cats respectively has also been associated with clinical cases. Chlamydophila conjunctivitis in cats should be differentiated from conjunctivitis caused by feline herpesvirus 1 and feline calicivirus.
Of particular interest were delayed reactions previously unreported in the literature in felines occurring 7 to 21 days after vaccination and the effect of concurrent vaccinations and cat age. PUREVAX Feline 4 is recommended for the vaccination of healthy cats 6 weeks of age and older for prevention of disease due to feline rhinotracheitis calici and panleukopenia viruses and as an aid in the reduction of disease due to Chlamydia psittaci. Chlamydial conjunctivitis in cats is caused by C felisC pneumoniae has also been detected in cats with conjunctivitis.
The safety profile of a new controlled-titer feline panleukopenia-rhinotracheitis-calicivirus-Chlamydia psittaci vaccine was compared to that of a currently-marketed vaccine. Give the first dose at least 60 days before ewes are exposed to rams followed by a second dose 30 days later. Noncore Vaccines for Cats.
Unfortunately it is not a part of the classic vaccination plan that most vets use so while they might make a recommendation to the pet owners they might not feel compelled to vaccinate their cats against Chlamydia. Feline Non-Core Vaccines Optional or non-core vaccines for cats consist of the vaccines for feline immunodeficiency virus Chlamydia felis and Bordetella bronchiseptica. For use in vaccinating healthy ewes to aid in the control of ovine enzootic abortion.
C suis is a cause of infectious conjunctivitis in pigs. FeLV is an important disease that can be spread through fighting through mutual. The vaccine does not completely protect the cat from infection but it can significantly reduce the severity and likelihood of infection.
Chlamydia Vaccine for Cats Overview. A quality core vaccine shown to be effective for vaccination of healthy cats 9 weeks of age or older against feline rhinotracheitis calici panleukopenia and feline leukemia viruses as well as feline Chlamydophila. Feline leukemia virus FeLV Chlamydophila felis Bordetella bronchiseptica FeLV Vaccine.
You may want to discuss with your veterinarian whether vaccination is appropriate for your cat. In some cases affected kittens may develop pneumonia. The FeLV vaccine works to protect your cat against feline leukemia virus.
If so your vet may decide to use a vaccine that does not contain a Chlamydia component in the future. Fel-O-Vax IV is for SQ vaccination of healthy cats 8-10 weeks of age or older against feline rhinotracheitis calici panleukopenia viruses and as an aid in the reduction of the severity of disease due to feline Chlamydia psittaci. The most common signs of chlamydia in cats involve the eyes or the upper respiratory tract nose or throat and only when infection is not treated does it spread to the lungs.
While it is listed as a noncore. Two doses are recommended. Vaccines that are appropriate for some cats in some circumstances are considered noncore vaccines or lifestyle vaccines.
Furthermore C psittaci has been found in numerous other mammalian species eg cattle swine horses small. Felis reduces the severity of clinical signs in. This bacteria has also been reported to infect the genital.
Chlamydiosis refers to a bacteria based chronic respiratory infection caused by the Chlamydia psittaci bacterium. Feline Chlamydophila formerly Chlamydia. Some vaccines have a Chlamydia component to them and some cats have been found to have reactions to that part of the vaccine.
Reconstitute the lyophilized vaccine with accompanying liquid diluent. Feline chlamydiosis also called feline pneumonitis is caused by the bacterial organism Chlamydophila felis. The duration of immunity against feline leukemia virus is at least 2 years.
With treatment the prognosis is positive. Order syringes needles for vaccines separately unless syringe is stated above. Core and non-core vaccinations 1 2 Core vaccines are those that all unvaccinated cats and cats with an unknown vaccination history should receive to protect them against key diseases including enteritis feline panleukopaenia a parvovirus and cat flu feline calicivirus and feline herpesvirus.
Infection as a serious cause of conjunctivitis in koalas is well documented. Some cats will develop a more severe reaction.

Upper Respiratory Infection Chlamydia In Cats Petmd

Nobivac Feline 1 Hcpch 25x1 Dose Upco Pet Supplies
Nobivac Feline 1 Hcpch 25x1 Dose Upco Pet Supplies

Nobivac Feline 1 Hcpch Eclipse 4 Revival Animal Health

Dog Vaccine Abbreviations Revival Animal Health

2020 Aaha Aafp Feline Vaccination Guidelines
/adult-cat-vaccination-schedule-4846632_V4-ff36ccb34d74410d9652b4307a26e8b3.png)
What Is The Average Adult Cat Vaccination Schedule

Chlamydial Conjunctivitis In Cats Vca Animal Hospital

What Vaccinations Should My Cat Receive Rspca Knowledgebase

Ragdoll Kitten Vaccination Which When To Vaccinate Catqueries
Kitten Growth Chart Registered Bengals
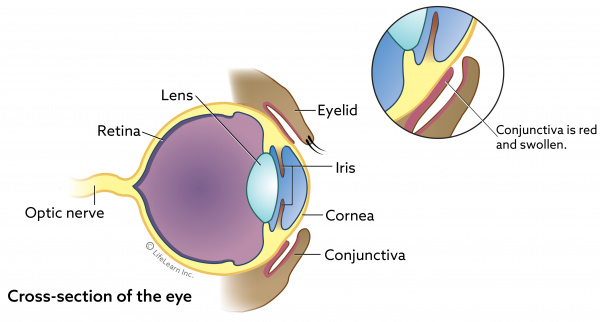
Chlamydial Conjunctivitis In Cats Vca Animal Hospital
Cat Kitten Vaccinations Advice Schedule Purina

Chlamydophila Felis Infection Feline Chlamydophilosis International Cat Care

Chlamydia In Cats A Common Cause Of Feline Conjunctivitis Kingsdale Animal Hospital

Chlamydia In Cats A Common Cause Of Feline Conjunctivitis Kingsdale Animal Hospital
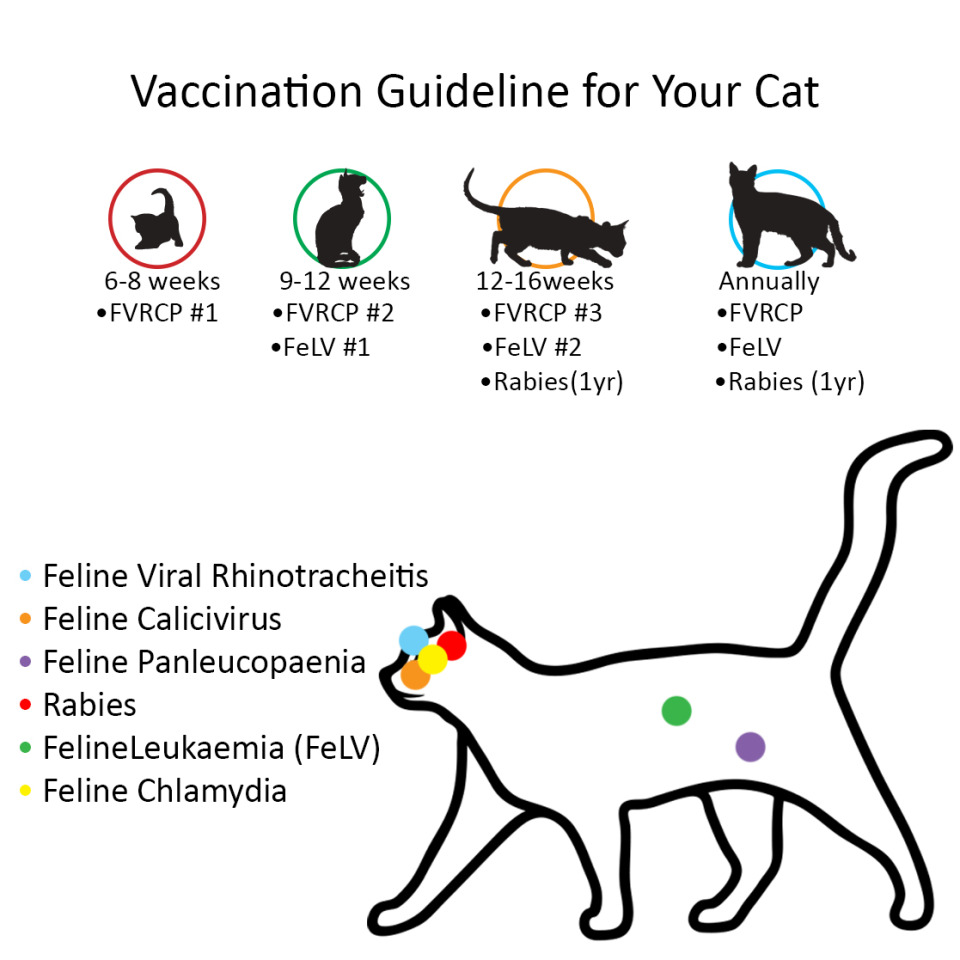
/kittens-GettyImages-119423835-f8a73e63994b4f36a0bff3953eacd04c.jpeg)